Can A Person With A Revoked License Register A Car
1.1. What is Cisco Smart Licensing?
Cisco Smart Licensing is a cloud-based unified license management system that manages all of the software licenses beyond Cisco products. It enables customers to purchase, deploy, manage, track and renew Cisco Software licenses. It also provides information about license ownership and consumption through a unmarried user interface
The solution is comprised of online Smart Accounts (at Cisco Smart Licensing Portal) used for tracking Cisco software avails and the Cisco Smart Software Director (CSSM) which is used to manage the Smart Accounts. CSSM is where all licensing management related tasks, such as registering, de-registering, moving, and transferring licenses tin be performed. Users can exist added and given admission and permissions to the smart account and specific virtual accounts.
1.two. Smart Licensing Implementation Methods
There are multiple methods in deploying Cisco Smart Licensing that can be leveraged depending on a company'south security profile such as:
Direct Cloud Admission
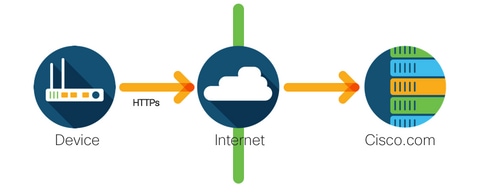
Cisco products ship usage information direct over the Internet securely using HTTPS. No additional components are needed.
Access through an HTTPS Proxy

Cisco products send usage information through an HTTP proxy server securely using HTTPS. An existing proxy server can be used or this can be deployed through Cisco'southward Transport Gateway.

On-premise License Server (Cisco Smart Software Manager satellite)
Cisco products send usage data to an on-premise server instead of directly over the internet. Once a calendar month the server reaches out over the internet for all devices via HTTPS or can be manually transferred to synchronize its database. CSSM Satellite is available as a Virtual Auto (VM) and can be downloaded hither.
one.iii. Supported IOS XE Platforms
- From sixteen.9.i release onwards, the Catalyst 3650/3850 and Catalyst 9000 serial switch platforms back up the Cisco Smart Licensing method as the only licensing method.
- From xvi.10.one release onwards, router platforms such as the ASR1K, ISR1K, ISR4K, and virtual routers (CSRv / ISRv) support the Cisco Smart Licensing method every bit the simply licensing method.
1.four. Migration fromLegacy Licenses to Smart Licenses
In that location are ii methods for converting a legacy license, similar Right-To-Use (RTU) or Production Activation Central (PAK) to a Smart License. For details on which method needs to be followed please refer to the relevant release notes and/or configuration guide for the specific Cisco device.
i.4.ane. Converting through Device Led Conversion (DLC)
- Device Led Conversion (DLC) is a ane-time method where the Cisco Product tin study what licenses it is using and the licenses are automatically deposited into their corresponding Smart Account on the Cisco Smart Software Director (CSSM). The DLC procedure is performed directly from the Command Line Interface (CLI) of the specific Cisco device.
- The DLC procedure is only supported on the Catalyst 3650/3850 and selected router platforms. For specific router models please refer to the individual platform configuration guide and release notes. Example: DLC process for Catalyst 3850 running Fuji 16.9.10 releases.
1.4.2. Converting through Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM) or License Registration Portal (LRP)
Cisco Smart Software Manager (CSSM) Method:
i. Login to Cisco Smart Software Director (CSSM) at https://software.cisco.com/
2. Navigate to Smart Software Licensing > Convert to Smart Licensing
three. Select Convert PAK or Convert Licenses
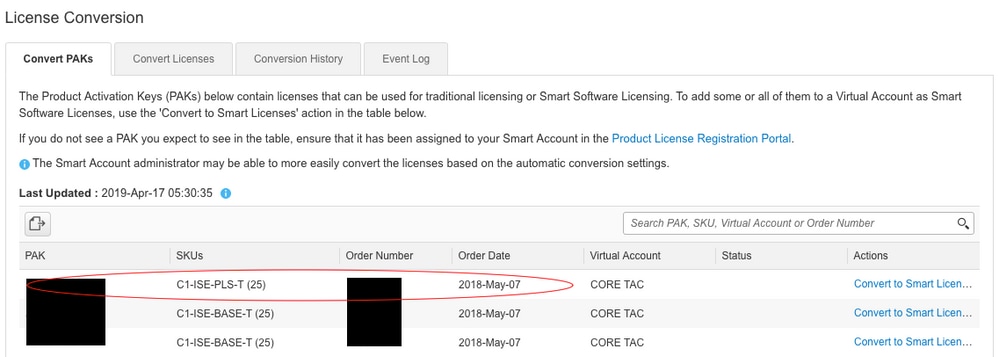
iv. Locate the license in the tabular array below if converting PAK license. If converting a non-PAK license use the"License Conversion Magician" for step by step directions.
Location of known PAK files associated with Business relationship:
Location of "License Conversion Wizard" link:
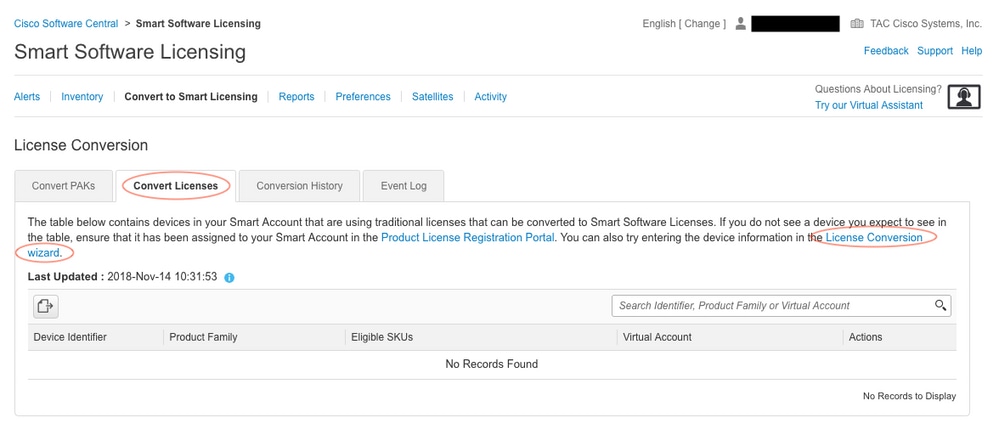
5. Locate the Desired License and Product combination
6. Click (under Actions): Convert to Smart Licensing
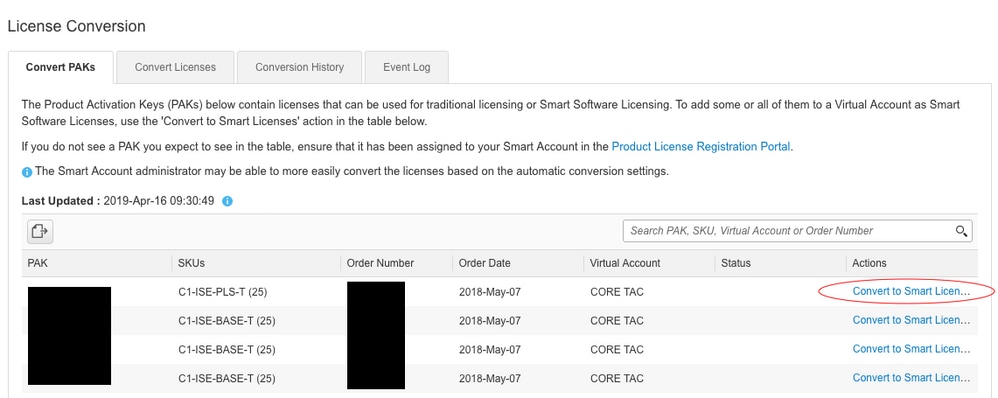
7. Select desired virtual account, license, and click Next
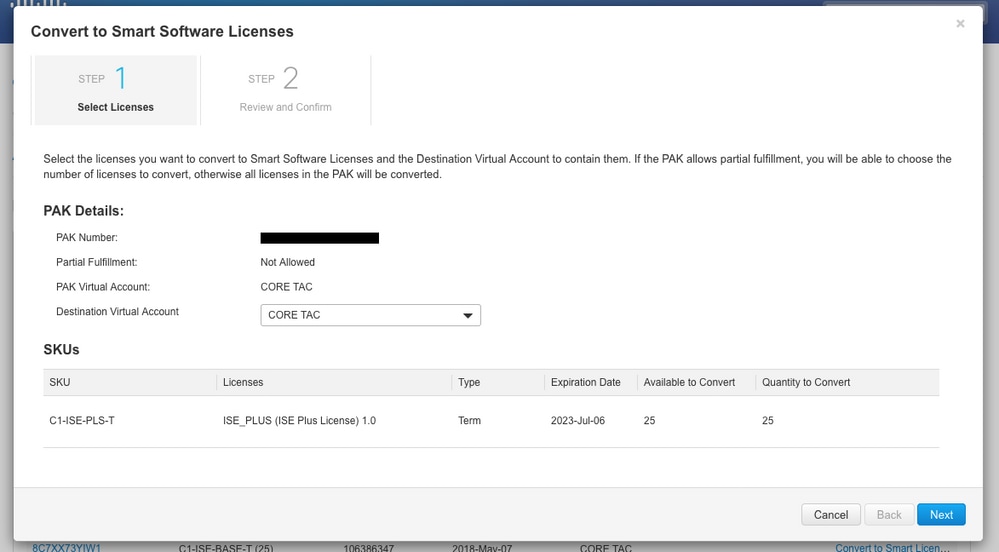
8. Review Selections, then click Convert Licenses
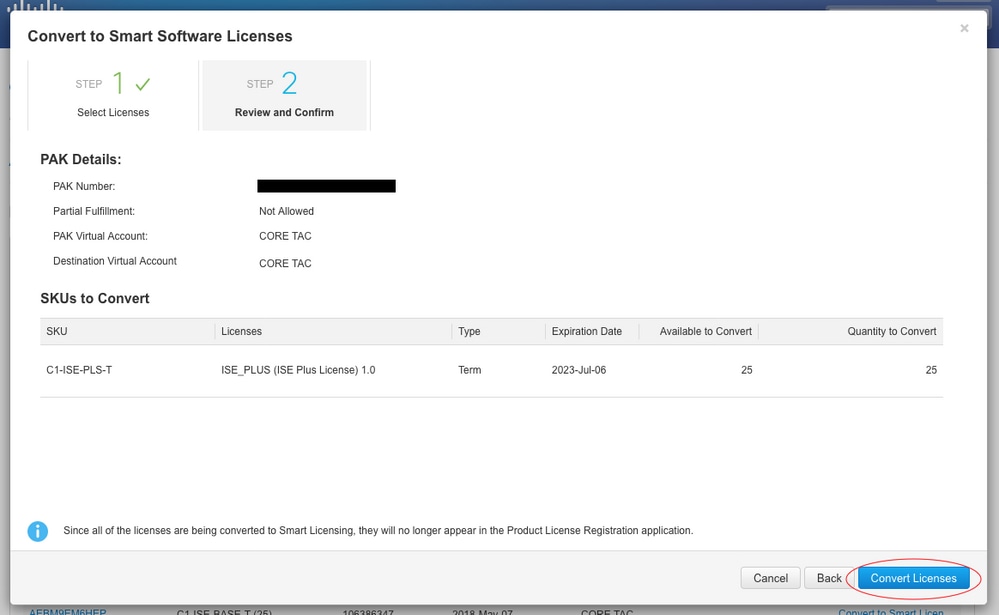
1.4.iii. Converting through contacting Cisco Global Licensing Operations (GLO) department
The Global Licensing Operations section tin exist reached here at our worldwide contact centers.
2.one. Bones configuration
Verbal procedure how to configure Smart Licensing can exist found in Arrangement Management Configuration Guide bachelor for each release / platform.
For instance: Arrangement Management Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Fuji xvi.nine.x (Catalyst 9300 Switches)
2.2. Registration Token / Device ID Token
Before registering device, Token needs to be generated. The registration token, also known as the device id token, is a unique token generated from the smart licensing portal or Cisco Smart Software Manager satellite when initially registering a Cisco device to the corresponding smart account. An individual token tin be used to register multiple Cisco devices depending on the parameters used during creation.
The registration token is as well merely required during initial registration of a Cisco device as it provides the data to the device to call-habitation to the Cisco back finish and exist tied to the correct Smart Business relationship. Subsequently the Cisco device is registered the token is no longer required.
2.3. Registration and License States
While deploying and configuring Smart Licensing in that location are multiple possible states that a Cisco device can be in. These states tin exist displayed by looking atshow license all orshow license statusfrom the Command Line Interface (CLI) of the Cisco device.
Below is a list of all states and their meaning:
- Evaluation (Unidentified) State
- This is a default land of the device when commencement booted.
- Usually, this state is seen when a Cisco device has not nonetheless been configured for Smart Licensing or registered to a Smart Business relationship.
- In this state all features are available and the device can freely change license levels.
- The evaluation flow is used when the device is in the unidentified state. The device will not attempt to communicate with Cisco in this state.
- This will be 90 days of usage and not 90 calendar days. In one case it is expired it is never reset.
- There is one evaluation menses for the entire device it is non per entitlement
- When the evaluation period expires at the end of 90 days, the device goes in to EVAL EXPIRY mode, withal in that location is no functional impact or disruption in functionality, even after reload. Currently at that place is no enforcement in place.
- The countdown fourth dimension is maintained across reboots.
- The evaluation period is used if the device has not yet registered with Cisco and has not received the following two messages from the Cisco backend:
- Successful response to a registration request
- Successful response to an entitlement authorization request.
- Registered State
- This is the expected state after successfully completing registration.
- The Cisco device has been able to successfully communicate with a Cisco Smart Account and annals.
- The device receives an ID certificate valid for 1 yr which volition be used for future communications
- The device will send a request to CSSM to authorize the entitlements for the licenses in employ on the device
- Depending on the CSSM response the device will and then enter Authorized or Out of Compliance
- The Id certificate expires at the end of ane yr. After 6 months the software Amanuensis process volition try to renew the certificate. If the Amanuensis cannot communicate with the Cisco Smart Software Managing director it will continue to try and renew the Id certificate until the expiration appointment (1 year). At the end of i twelvemonth, the agent will go dorsum to the Un-Identified state and volition try to enable the Evaluation period. The CSSM will remove the production example from its database.
- Authorized State
- This is the expected state when device is using an entitlement and is in Compliance (no negative balance),
- The Virtual Business relationship on CSSM had the correct type and number of licenses to authorize the consumption of the device's licenses
- At the end of 30 days, the device will transport a new request to CSSM to renew the authorization.
- Has a time span of 90 days later which (if not successfully renewed) is moved to Authorization Expired state.
- Out of Compliance Country
- This is the state when device is using an entitlement and is not in Compliance (negative balance),
- This country is seen when the license does not have an available license in the corresponding Virtual Account that the Cisco device is registered to in the Cisco Smart Account.
- To enter into Compliance / Authorized state, a customer must add the correct number and blazon of licenses to the Smart Business relationship
- When in this land the device will automatically send an authorization renewal request every day
- Licenses and features will continue to operate and there is no functional impact
- Authorization Expired State
- This is the state when device is using an entitlement has non been able to communicate with the Cisco Smart Account associated for over 90 days.
- This is typically seen if the Cisco device loses cyberspace access or cannot connect to tools.cisco.com subsequently initial registration.
- Online methods of smart licensing crave Cisco devices to communicate a minimum of every 90 days to prevent this status.
- CSSM volition return all in use licenses for this device dorsum to the pool since it has non had any communications for ninety days
- While in this state the device will go along to try to contact Cisco, every hr, to renew the entitlement authorization, until the registration menstruation (id document) expires
- If the software Agent re-establishes communications with Cisco and receives to its request for authorization information technology volition process that reply unremarkably and enter into 1 of the established states
- Starting in 16.nine.one for switches and sixteen.10.1 for routers, a default Call-home profile named "CiscoTAC-1" is generated to assist with migrating to Smart Licensing. Past default, this profile is fix up for the Directly Deject Admission method.
#show telephone call-home profile CiscoTAC-1 Profile Name: CiscoTAC-ane Profile status: ACTIVE Profile mode: Full Reporting Reporting Data: Smart Telephone call Dwelling house, Smart Licensing Preferred Message Format: xml Message Size Limit: 3145728 Bytes Ship Method: http HTTP accost(es): https://tools.cisco.com/its/service/oddce/services/DDCEService Other address(es): default <snip>
- When utilizing a Cisco Smart Software Managing director satellite, the destination address under the active call-abode configuration must point to it (instance-sensitive!):
(config)#call-dwelling
(cfg-call-habitation)#profile "CiscoTAC-1"
(cfg-phone call-domicile-profile)#destination address http https://<IP/FQDN>/TransportGateway/services/DeviceRequestHandler
- If DNS needs to exist resolved in a VRF, then DNS can be configured in the following way:
(config)#ip domain-lookup [source-interface <INTERFACE>]
(config)#ip name-server [vrf <VRF>] <IP>
Alternatively, if DNS is not available, statically configure local DNS to IP mapping (based on local DNS resolution on your stop-device) or supervene upon DNS name in phone call-abode configuration with IP accost. Refer to example for directly deject admission (for Cisco Smart Software Manager satellite utilize its own DNS name instead of tools.cisco.com):
(config)#ip host tools.cisco.com 173.37.145.8
- If communication totools.cisco.comneeds to be originated from the interface in specific VRF (e.chiliad. Mgmt-vrf), and so the post-obit CLI needs to be configured:
(config)#ip http client source-interface <VRF_INTERFACE>
- A different number of licenses might exist consumed depending on the configuration of the Cisco device such every bit with Catalyst switches running in StackWise or StackWise Virtual:
Traditional Stack-wise Supported Switches (e.m. Catalyst 9300 series):
Network License: 1 license is consumed per switch in the stack
DNA License: ane license is consumed per switch in the stack
Modular Chassis (e.yard. Catalyst 9400 series):
Network License: 1 license is consumed per supervisor in the chassis
DNA License: 1 license is consumed per chassis
Fixed Stack-wise Virtual Supported Switches (eastward.g. Catalyst 9500 series):
Network License: one license is consumed per switch in the stack
Deoxyribonucleic acid License: ane license is consumed per switch in the stack
- Simply 1 call-home profile can be active for Smart Licensing.
- Licenses are simply consumed if a corresponding feature is configured.
- Cisco devices configured for Smart Licensing need to be configured with the right system time and appointment to ensure they are properly synchronized with the respective Cisco Smart Account. If the time starting time of the Cisco device is too far off it, the device tin can neglect to register. The clock volition demand to exist manually set or configured via a timing protocol such as Network Time Protocol (NTP) or Precision Time Protocol (PTP). For the exact steps required to implement these changes delight refer to the configuration guide for the specific Cisco device.
- The Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) central generated during the Cisco device registration needs to be saved if information technology is not automatically saved later on registration. If the device fails to save the PKI cardinal and so a syslog is generated stating to save the configuration via "copy running-config startup-config" or "write memory".
- If the PKI key of the Cisco device is not properly saved, and then the license country can be lost on failovers or reloads.
- Smart Licensing does not support HTTPS Proxy SSL certificate interception past default when using 3rd party proxies for the HTTPS Proxy method. To back up this feature, you lot can either disable SSL interception on the Proxy, or manually import the certification sent from the Proxy.
How to Manually Import Certification as a TrustPoint:
Note, the document will demand exist in a BASE64 format to be copied and pasted onto the device as a TrustPoint.The following example shown below uses "LicRoot" as the TrustPoint name, however, this proper noun tin be changed equally desired.
Device#conf t
Device(config)#crypto pki trustpoint LicRoot
Device(ca-trustpoint)#enrollment terminal
Device(ca-trustpoint)#revocation-check none
Device(ca-trustpoint)#exit
Device(config)#crypto pki authenticate LicRoot
Enter the base 64 encoded CA document.
Finish with a blank line or the discussion "quit" on a line by itself
-----Begin CERTIFICATE-----
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
-----END Document-----
Document has the following attributes:
Fingerprint MD5: XXXXXXXX
Fingerprint SHA1: XXXXXXX
% Do you take this certificate? [yes/no]: yes
Trustpoint CA certificate accustomed.
% Certificate successfully imported
- When using the Ship Gateway HTTP Proxy the IP accost needs to exist changed from tools.cisco.com to the Proxy like the following:
destination accost http https://tools.cisco.com/its/service/oddce/services/DDCEService
TO
destination address http https://<TransportGW-IP_Address>:<port_number>/TransportGateway/services/DeviceRequestHandler - The Transport Gateway IP accost can found by navigating to the HTTP Settings and looking under the HTTP Service URLs on the Cisco Ship Gateway GUI.
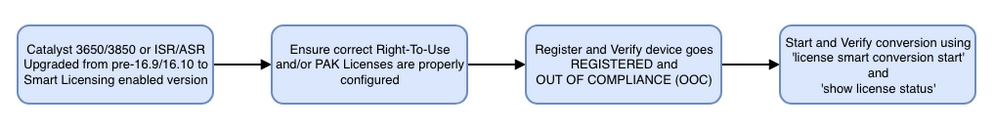
When migrating a Cisco device to a Smart Licensing enabled software version the following flowchart tin be used as a general guide for all three methods (Directly Cloud Access, HTTPS Proxy, and Cisco Smart Software Managing director satellite).
Device Upgraded or Shipped with software release that supports Smart Licensing (refer to section ane.iii for list of supported IOS-XE releases).
Below troubleshooting steps mainly concentrate on a scenario in which 'device fails to register'.
four.i. Device Fails to register
Later initial configuration, in lodge to enable Smart Licensing, Token, which is generated on CSSM / Cisco Smart Software Director satellite, needs to be registered on the device via CLI:
license smart register idtoken <TOKEN>
This should generate the following events:
!
! Smart licensing process starts
!
Registration process is in progress. Use the 'prove license status' command to check the progress and result !
! Crypto primal is automatically generated for HTTPS communication
!
Generating 2048 flake RSA keys, keys volition be exportable... [OK] (elapsed time was ane seconds) %CRYPTO_ENGINE-5-KEY_ADDITION: A fundamental named SLA-KeyPair has been generated or imported by crypto-engine %PKI-4-NOCONFIGAUTOSAVE: Configuration was modified. Issue "write retention" to save new IOS PKI configuration !
! Call-home beginning registration process
! %CALL_HOME-6-SCH_REGISTRATION_IN_PROGRESS: SCH device registration is in progress. Call-dwelling house volition poll SCH server for registration effect. You can also check SCH registration status with "call-home asking registration-info" under EXEC fashion. !
! Smart Licensing procedure connects with CSSM and cheque entitlement.
! %SMART_LIC-6-EXPORT_CONTROLLED: Usage of export controlled features is allowed %SMART_LIC-6-AGENT_REG_SUCCESS: Smart Amanuensis for Licensing Registration with the Cisco Smart Software Manager or satellitefor udi PID:<PID>,SN:<SN> %SMART_LIC-4-CONFIG_NOT_SAVED: Smart Licensing configuration has non been saved %SMART_LIC-5-IN_COMPLIANCE: All entitlements and licenses in utilize on this device are authorized %SMART_LIC-6-AUTH_RENEW_SUCCESS: Authorization renewal with the Cisco Smart Software Manager or satellite. Country=authorized for udi PID:<PID>,SN:<SN>
To check phone call-home configuration, run the post-obit CLI:
#bear witness call-dwelling profile all Profile Name: CiscoTAC-1 Profile status: ACTIVE Profile manner: Total Reporting Reporting Data: Smart Phone call Home, Smart Licensing Preferred Message Format: xml Message Size Limit: 3145728 Bytes Ship Method: http HTTP address(es): https://tools.cisco.com/its/service/oddce/services/DDCEService Other address(es): default Periodic configuration info message is scheduled every 1 twenty-four hour period of the month at 09:15 Periodic inventory info message is scheduled every i day of the month at 09:00 Warning-grouping Severity ------------------------ ------------ crash debug diagnostic minor environment alert inventory normal Syslog-Pattern Severity ------------------------ ------------ APF-.-WLC_.* warning .* major
To check Smart Licensing status, run the following CLI:
#show license summary Smart Licensing is ENABLED Registration: Condition: REGISTERED Smart Account: TAC Cisco Systems, Inc. Virtual Account: Krakow LAN-SW Export-Controlled Functionality: Immune Concluding Renewal Attempt: None Adjacent Renewal Attempt: Nov 22 21:24:32 2019 UTC License Authorization: Status: AUTHORIZED Last Advice Attempt: SUCCEEDED Adjacent Communication Endeavor: Jun 25 21:24:37 2019 UTC License Usage: License Entitlement tag Count Status ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- C9500 Network Advantage (C9500 Network Advantage) 1 AUTHORIZED C9500-DNA-40X-A (C9500-40X Deoxyribonucleic acid Advantage) 1 AUTHORIZED
In case device neglect to annals (and Status is different from REGISTERED every bit shown above; note that Out-of-Compliance points to an issue on CSSM like missing license in Smart Virtual Business relationship, wrong mapping (i.due east. Token from different virtual account was used where licenses are not available, etc.) cheque the following:
1. Verify configuration settings and common failure scenarios
Refer to department 2.1 for basic configuration steps. Look also at section 5 for mutual failure scenarios observed in the field.
2. Check basic connectivity
Verify that device tin reach (and open TCP port) to tools.cisco.com (in case of direct access) or to Cisco Smart Software Manager satellite:
#show run all | in destination address http destination address http https://tools.cisco.com/its/service/oddce/services/DDCEService ! ! check connectivity ! #telnet tools.cisco.com 443 /source-interface gi0/0 Trying tools.cisco.com (173.37.145.eight, 443)... Open [Connexion to tools.cisco.com closed by foreign host]
In case above does not work, double-cheque your routing rules, source-interface and firewall settings.
Note that HTTP (TCP/80) is being deprecated and the recommended protocol is HTTPS (TCP/443).
Refer to section: "3. Considerations and Caveats" in this document for further guidelines how to configure DNS and HTTP details.
3. Verify Smart License settings
Collect the output of:
#show tech-back up license
and validate nerveless configuration / logs (attach this output in instance y'all decide to open Cisco TAC case for further investigation).
4. Enable debugs
Enable the following debugs to collect additional information about Smart Licensing process (note that after enabing debugs, you need to try to register license once once more via CLi mentioned in bespeak 4.1):
#debug call-abode smart-licensing [all | trace | error] #debug ip http customer [all | api | cache | fault | chief | msg | socket]
For internal debugs, enable and read binary traces:
! enable debug #set platform software trace ios [switch] active R0 infra-sl debug ! ! read binary traces infra-sl process logs #testify platform software trace bulletin ios [switch] agile R0
The following are some common failure scenarios that could be experienced during or after a Cisco device registration:
Scenario #1: Switch Registration "Failure Reason: Product Already Registered"
Snip of "show license all":
Registration:
Status:UNREGISTERED – REGISTRATION FAILED
Export-Controlled Functionality: NotAllowed
Initial Registration: FAILED on Oct 22 14:25:31 2018 EST
Failure reason:Product Already Registered
Next Registration Effort: Oct 22 14:45:34 2018 EST
Next Steps:
– The Cisco device will demand to be registered again.
– If the Cisco device is seen in the Cisco Smart Software Managing director (CSSM), the "force" parameter will need to be used (i.e. "license smart register idtoken <TOKEN> forcefulness")
Annotation:The failure reason can besides testify as the following:
– Failure reason: The product <X> and sudi containing udiSerialNumber:<SerialNumber>,udiPid:<Production> has already been registered.
– Failure reason: Existing Product Instance has Consumption and Strength Flag is False
Scenario #2: Switch Registration "Failure Reason: Your request could not exist processed right now. Please try once more"
Snip of "show license all":
Registration:
Status: REGISTERING – REGISTRATION IN PROGRESS
Export-Controlled Functionality: NotAllowed
Initial Registration: FAILED on Oct 24 15:55:26 2018 EST
Failure reason:Your asking could non be processed correct at present. Delight try once again
Next Registration Attempt: Oct 24 16:12:xv 2018 EST
Next Steps:
– Enable debugs every bit mentioned in section 4 to go more insights on the outcome,
– Generate new Token in CSSM in your Smart Licensing and take an another attempt.
Scenario #iii: Failure Reason "The device date 1526135268653 is offset beyond the immune tolerance limit
Snip of "evidence license all":
Registration:
Status: REGISTERING – REGISTRATION IN PROGRESS
Export-Controlled Functionality: NotAllowed
Initial Registration: FAILED on November 1117:55:46 2018 EST
Failure reason:{"timestamp":["The device appointment '1526135268653' is offset beyond the allowed tolerance limit."]}
Side by side Registration Try: Nov 11 18:12:17 2018 EST
Possible Logs Seen:
%PKI-3-CERTIFICATE_INVALID_NOT_YET_VALID: Document chain validation has failed. The certificate (SN: XXXXXX) is not nonetheless valid. Validity period starts on 2018-12-12:43Z
Next Steps:
– Verify that the Cisco device clock is showing the correct time (show clock)
– Configure the Network Time Protocol (NTP) if possible to ensure the clock is set correctly
– If NTP is not possible, verify that the manually set clock (clock set) is correct (show clock) and configured equally a trusted fourth dimension source by verifying that "clock agenda-valid" is configured
NOTE– Past default, the system clock is not trusted. "clock calendar-valid" is required.
Scenario #4: Switch Registration "Failure Reason: Communication transport non bachelor."
Snip of "show license all":
Registration: Condition: UNREGISTERED – REGISTRATION FAILED
Export-Controlled Functionality: Not Allowed
Initial Registration: FAILED on Mar 09 21:42:02 2019 CST
Failure reason:Communication transport not available.
Possible Logs Seen:
%CALL_HOME-3-CALL_HOME_FAILED_TO_ENABLE: Failed to enable call-domicile from Smart Agent for Licensing: The command failed to enable smart telephone call abode due to an existing agile user profile. If yous are using a user profile other than "CiscoTAC-one" profile to send data to SCH server in Cisco, delight enter "reporting smart-licensing-data" under profile way to configure that profile for smart licensing. For more details near SCH, delight check http://world wide web.cisco.com/go/smartcallhome
%SMART_LIC-3-AGENT_REG_FAILED: Smart Agent for Licensing Registration with the Cisco Smart Software Manager or satellite failed: Communication transport not available.
%SMART_LIC-3-COMM_FAILED: Communications failure with the Cisco Smart Software Manager or satellite: Communication send not available.
Next Steps:
– Verify that call-home is enabled with "service call-domicile" in the "evidence running-config" output of the Cisco device
– Ensure that the right phone call-dwelling profile is active
– Verify that "reporting smart-licensing-information" is configured nether the active call-dwelling profile
Scenario #5: Switch License Authorization "Failure reason: Fail to ship out Call Home HTTP message."
Snip of "show license all":
License Authorization:
Status: OUT OF COMPLIANCE on Jul 26 09:24:09 2018 UTC
Last Communication Attempt: FAILED on Aug 02 xiv:26:23 2018 UTC
Failure reason:Fail to send out Call Habitation HTTP message.
Adjacent Advice Attempt: Aug 02 14:26:53 2018 UTC
Advice Deadline: October 25 09:21:38 2018 UTC
Possible logs are seen:
%SMART_LIC-3-COMM_FAILED:Communications failure with the Cisco Smart Software Manager or satellite: Fail to send out Telephone call Home HTTP message.
%SMART_LIC-3-AUTH_RENEW_FAILED:Dominance renewal with the Cisco Smart Software Manager or satellite: Communication message transport error for udi PID:XXX, SN: Xxx
Next Steps:
– Verify that the Cisco device can pingtools.cisco.comor the nslookup translated IP
– Try to telnet from the Cisco device to tools.cisco.com on TCP port 443 (port used by HTTPS)
– Verify that the HTTPs customer source interface is correct
– Verify that the URL/IP in the phone call abode profile is gear up correctly on the Cisco device via"show telephone call-home profile all"
– Verify the ip route is pointing to the correct next hop
– EnsureTCP port 443is not existence blocked on the Cisco device, the path to Smart Call Home Server, or the Cisco Smart Software Director satellite
– Ensure that the correct Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) instance is configured if applicable
Scenario #6: Switch License Authorization "Failure reason: Waiting for reply"
Snip of "show license all":
License Authorisation:
Condition: OUT OF COMPLIANCE on Jul 26 09:24:09 2018 UTC
Last Communication Attempt: PENDING on Aug 02 fourteen:34:51 2018 UTC
Failure reason: Waiting for respond
Next Advice Attempt: Aug 02 14:53:58 2018 UTC
Communication Deadline: Oct 25 09:21:39 2018 UTC
Possible logs are seen:
%PKI-3-CRL_FETCH_FAIL: CRL fetch for trustpoint SLA-TrustPoint failed Reason : Failed to select socket. Timeout : 5 (Connection timed out)
%PKI-3-CRL_FETCH_FAIL: CRL fetch for trustpoint SLA-TrustPoint failed Reason : Failed to select socket. Timeout : 5 (Connection timed out)
Next Steps:
– To correct this result the SLA-TrustPoint should be configured asnone under the running configuration
show running-config
<omitted>
crypto pki trustpoint SLA-TrustPoint
revocation-checknone
What is a CRL?
A Certificate Revocation List (CRL) is a list of revoked certificates. The CRL is created and digitally signed by the certificate potency (CA) that originally issued the certificates. The CRL contains dates for when each document was issued and when it expires. Further information in regards to CRL is available here.
Scenario #vii: License in "OUT OF COMPLIANCE" status
Snip of "bear witness license all":
License Authorization:
Condition: OUT OF COMPLIANCE on Jul 26 09:24:09 2018 UTC
Last Communication Attempt: Awaiting on Aug 02 xiv:34:51 2018 UTC
Failure reason: Waiting for answer
Next Advice Attempt: Aug 02 14:53:58 2018 UTC
Communication Deadline: Oct 25 09:21:39 2018 UTC
Possible logs are seen:
%SMART_LIC-3-OUT_OF_COMPLIANCE: Ane or more entitlements are out of compliance
Next Steps:
– Verify if Token from proper Smart Virtual Business relationship has been used,
– Verify amount of available licenses here.
Source: https://blog.octanetworks.com/cisco-smart-licensing-troubleshooting-steps-and-considerations-on-catalyst-platforms/
Posted by: sussmanciary1980.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Can A Person With A Revoked License Register A Car"
Post a Comment